3/28
Can plant-based products be used in durable goods?
When it comes to plant-based products, consumers often think of single use items like bags, boxes, and take-out containers. A growing sustainability movement has introduced shoppers to the world of products made from renewable inputs and all the benefits that come with them. But what many consumers don’t realize is that plant-based materials can be used in more durable, long-lasting products – everything from car parts to construction and building materials to electronics and more. Our latest blog post takes a look at how plant-based materials can be used to create products that will last for years to come.
Renewable Inputs
Before we begin, let’s get a reminder on how plant-based products are developed. A variety of renewable inputs, including corn, agricultural waste materials, grasses, and algae, are used to produce a wide range of products. Manufacturers and chemists innovate processes that are specific to each product, providing each one with different, unique functionality. Some plant-based alternatives serve as drop-in replacements for traditional products, while others have entirely new properties. And, many plant-based products are recyclable or compostable, starting the process over again.
Now, let’s explore the different ways plant-based products can be used to create durable products.
Automotive Parts
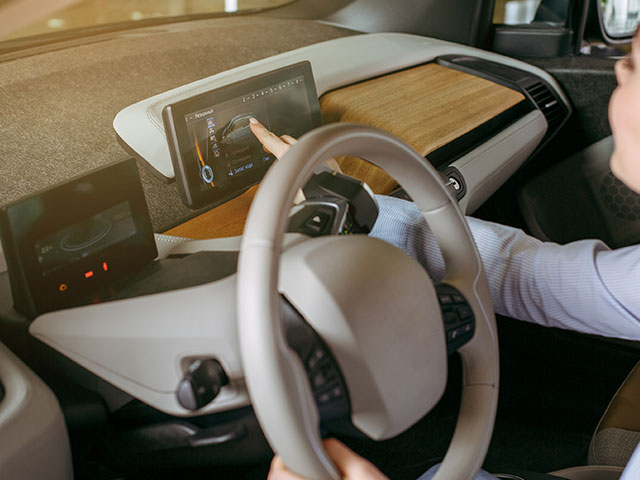
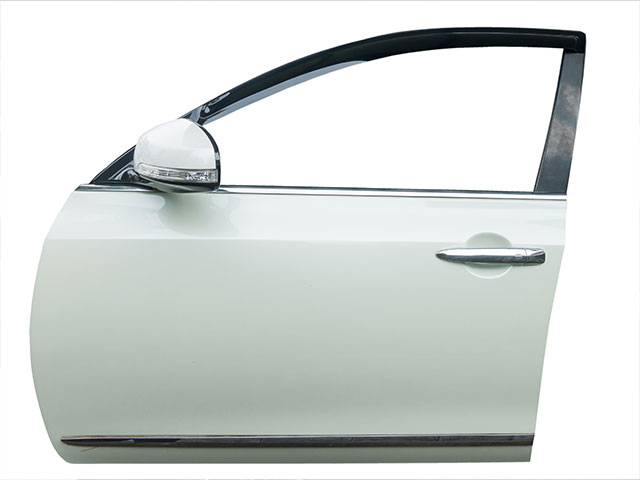
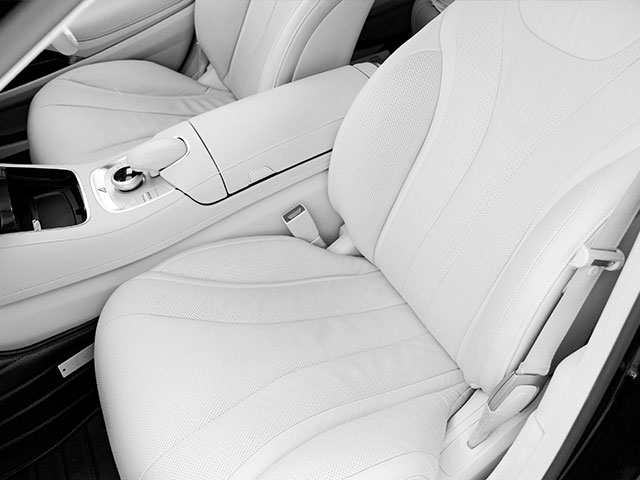
Plant-based vehicles and car parts are having their moment in the sun as researchers develop new ways to incorporate products from renewable inputs into the automotive industry. Hemp has long been used to develop interior automotive parts like door panels and dashboards, and more and more car manufacturers are jumping onto this trend. From polymer composites made from grass fibers to seat cushions developed from ‘mushroom leather,’ automotive makers are creatively finding ways to incorporate more sustainable features that are designed to last. There’s even been a car developed entirely from plant-based products – with lighter weight components, the cars boast improved fuel efficiency, which leads to a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions. Although plant-based cars aren’t ready for the market just yet, these innovations demonstrate the potential opportunities that exist.
Durable Materials
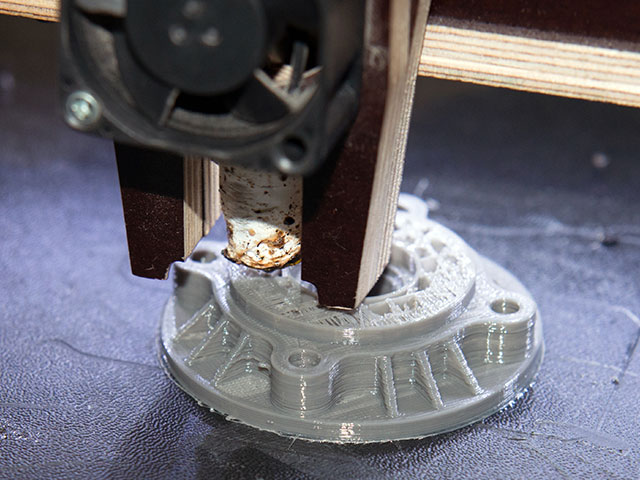
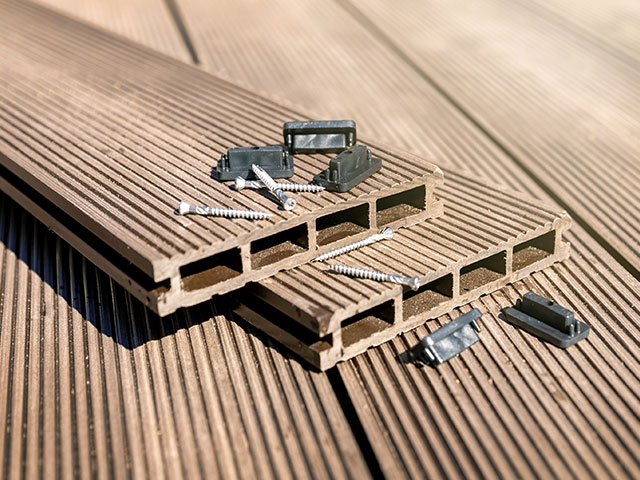
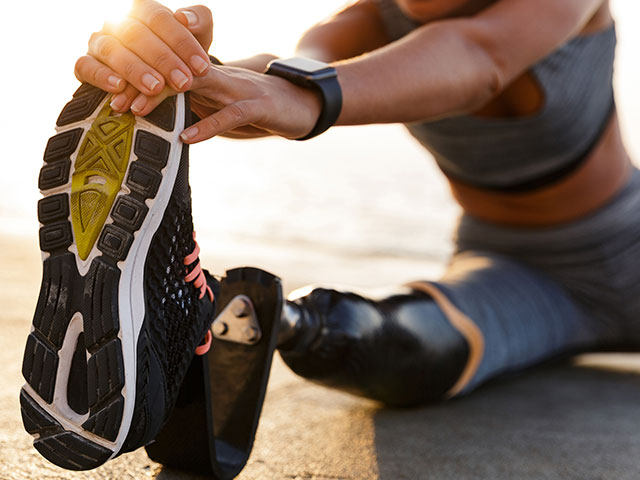
Advancements in manufacturing have created a plethora of plant-based material options that can be used in a wide variety of durable products. Using 3D printing techniques, researchers developed a printable composite using synthetic plastic and nanocrystals, leading to a material tougher than bone and harder than aluminum. Insulating underlay, construction materials for outdoor decks, wall coverings, and paint are all created using plant-based products. Hemp materials have even been used to manufacture prosthetics!
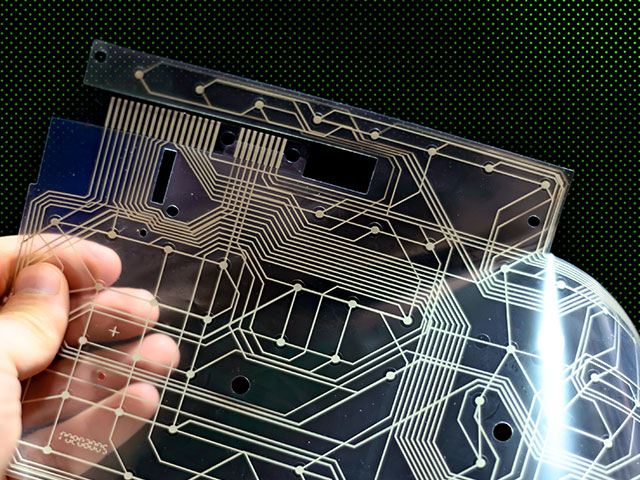
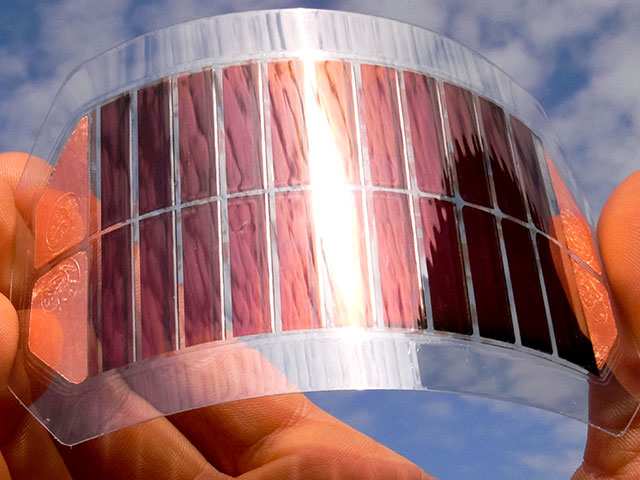
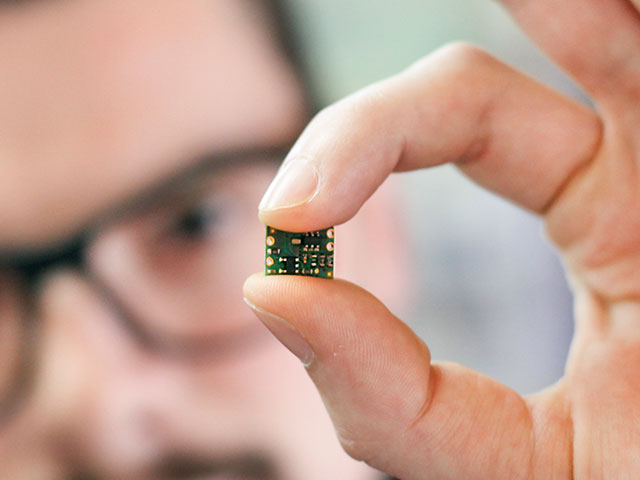
Sustainable Electronics
Creating parts from plant-based materials represents the future of sustainable electronics. The tech industry has long struggled with waste when it comes to creating the materials, but leaders in the plant-based movement have formulated new approaches to create real opportunity for increased circularity across the industry. Exciting innovations like plant-based actuators offer a glimpse into a greener tech world. Researchers with an eye on waste management have even been working on biodegradable electronics to help us break the cycle of tossing old devices into landfills.
Bringing Jobs to Small Communities
As innovation moves forward, increased production of these products help bring economic opportunity to America, particularly in our country’s heartland. The plant-based products industry brings jobs to small communities and contributes to quality-of-life improvements—both economically and environmentally. Biorefineries and industry facilities are frequently located near agricultural feedstocks in rural America, creating a need for everything from tradespersons to chemists and engineers.
The wide-ranging uses of plant-based products offer significant potential – and it gets even more exciting when the environmental benefits they bring are fully realized. Unlike traditional materials derived from fossil fuels, feedstocks from plant-based materials remove carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere during their growing phase, and some is sequestered in the materials during their time as a useful consumer product. Plus, the various end-of-life options available expand circularity, meaning that products stay out of landfills and produce less greenhouse gas emissions. Incorporating more plant-based products into all of our purchasing choices goes a long way towards creating a more circular, sustainable future.